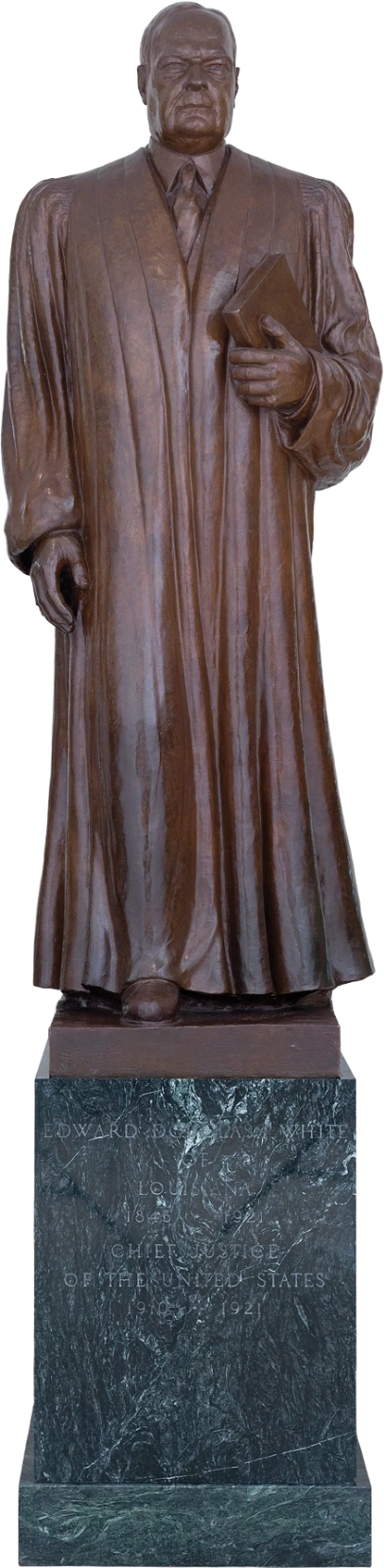
Edward Douglass White
Capitol Visitor Center
Arthur C. Morgan (1955)

About This Statue
Edward Douglas White was born on November 3, 1845, in Louisiana. He was educated at Mount St. Mary's College in Maryland; at Jesuit College in New Orleans; and at Georgetown College (now University) in Washington, D.C. In 1861 he left school and enlisted in the Confederate Army. After the war he studied law, and in 1868 he was admitted to the bar.
- He served in the state Senate from 1874 to 1879 and on the Louisiana Supreme Court from 1879 to 1880.
- He was elected to the U.S. Senate in 1890 and served until 1894, when he was appointed to the Supreme Court by President Cleveland.
- Appointed chief justice by President Taft in 1910, he was the first justice to be so elevated, and he served until his death.
- White's 27 years on the high court spanned a period of rapid social and economic change, including the development and expansion of the powers of the federal government.
- His commitment to nationalism was particularly evident in decisions regarding congressional power over interstate commerce.
- His major contribution to jurisprudence was the 1911 "rule of reason" decision, applied to anti-trust cases. He also supported a federal income tax.
- White died in Washington, D.C., on May 19, 1921.in Louisiana. He was educated at Mount St. Mary's College in Maryland; at Jesuit College in New Orleans; and at Georgetown College (now University) in Washington, D.C. In 1861 he left school and enlisted in the Confederate Army. After the war he studied law, and in 1868 he was admitted to the bar.
- He served in the state Senate from 1874 to 1879 and on the Louisiana Supreme Court from 1879 to 1880.
- He was elected to the U.S. Senate in 1890 and served until 1894, when he was appointed to the Supreme Court by President Cleveland.
- Appointed chief justice by President Taft in 1910, he was the first justice to be so elevated, and he served until his death.
- White's 27 years on the high court spanned a period of rapid social and economic change, including the development and expansion of the powers of the federal government.
- His commitment to nationalism was particularly evident in decisions regarding congressional power over interstate commerce.
- His major contribution to jurisprudence was the 1911 "rule of reason" decision, applied to anti-trust cases. He also supported a federal income tax.
- White died in Washington, D.C., on May 19, 1921.